Bring Data to Life: How to Install Grafana on Ubuntu 22.04

Monitoring and visualizing real-time data has become crucial for businesses to make data-driven decisions. Several tools exist to achieve this goal, including paid ones. Grafana is one such tool; however, it's free and open-source. It stands out from other analytics tools with its flexibility to connect to a wide range of data sources and its highly customizable, interactive dashboards. Unlike many paid tools, Grafana's open-source model provides powerful visualization at no cost, making it a scalable choice for teams of all sizes.
In this guide, we'll cover the step-by-step installation process of Grafana using the official Grafana APT repository. Let's dive into the process to get your Grafana instance up and running.
Prerequisites
- A Virtual Machine (such as the ones provided by NodeShift) with at least:
- 2 vCPUs
- 2 GB RAM
- 10 GB SSD
- Ubuntu 22.04 VM
Note: The above prerequisites are highly variable across use cases. A high-end configuration should be used for a large-scale deployment.
Step-by-step process to install Grafana on Ubuntu 22.04
For this tutorial, we'll use a CPU-powered Virtual Machine by NodeShift, which provides high-compute Virtual Machines at a very affordable cost on a scale that meets GDPR, SOC2, and ISO27001 requirements. Also, it offers an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it easier for beginners to get started with Cloud deployments. However, feel free to use any cloud provider you choose and follow the same steps for the rest of the tutorial.
Step 1: Setting up a NodeShift Account
Visit app.nodeshift.com and create an account by filling in basic details, or continue signing up with your Google/GitHub account.
If you already have an account, login straight to your dashboard.
Step 2: Create a Compute Node (CPU Virtual Machine)
After accessing your account, you should see a dashboard (see image), now:
- Navigate to the menu on the left side.
- Click on the Compute Nodes option.
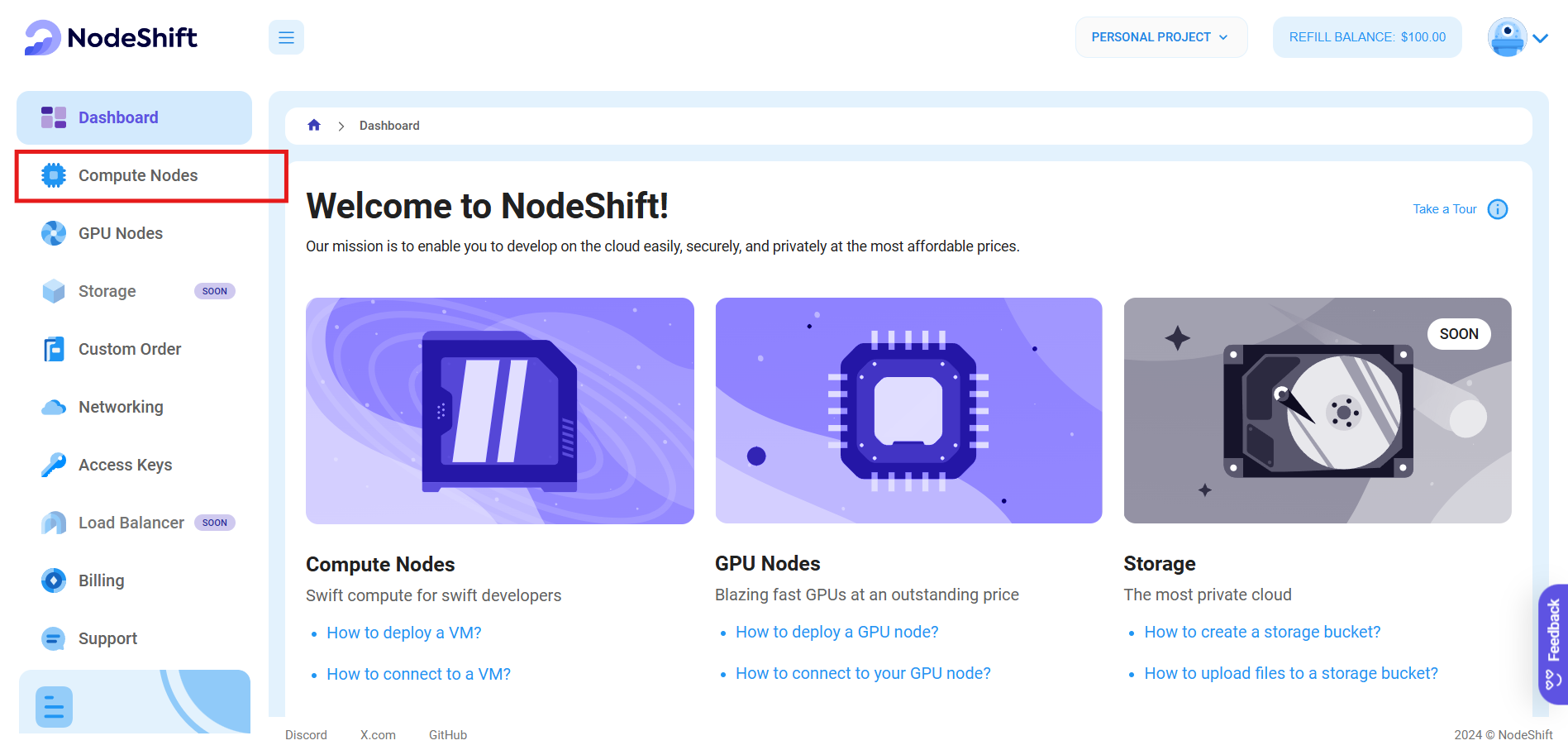
- Click on Start to start creating your very first compute node.

These Compute nodes are CPU-powered virtual machines by NodeShift. These nodes are highly customizable and let you control different environmental configurations, such as vCPUs, RAM, and storage, according to your needs.
Step 3: Select configuration for VM
- The first option you see is the Reliability dropdown, which lets you choose the type of uptime guarantee level you're seeking for your VM (e.g., 99%).

- Next, select a geographical region from the Region dropdown where you want to launch your VM (e.g., United States).
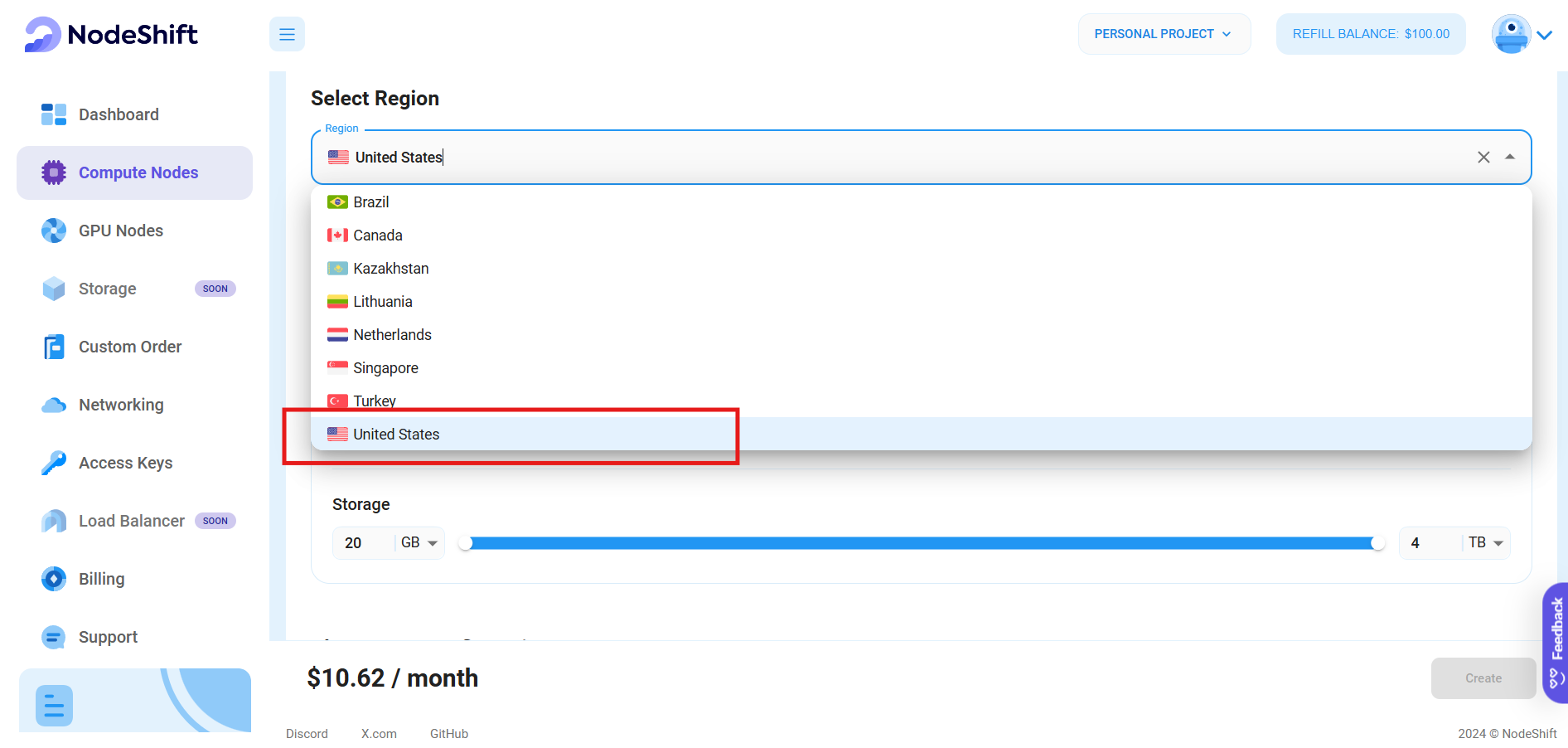
- Most importantly, select the correct specifications for your VM by sliding the bars for each option. We'll choose the specifications per the "Prerequisites" for this tutorial.
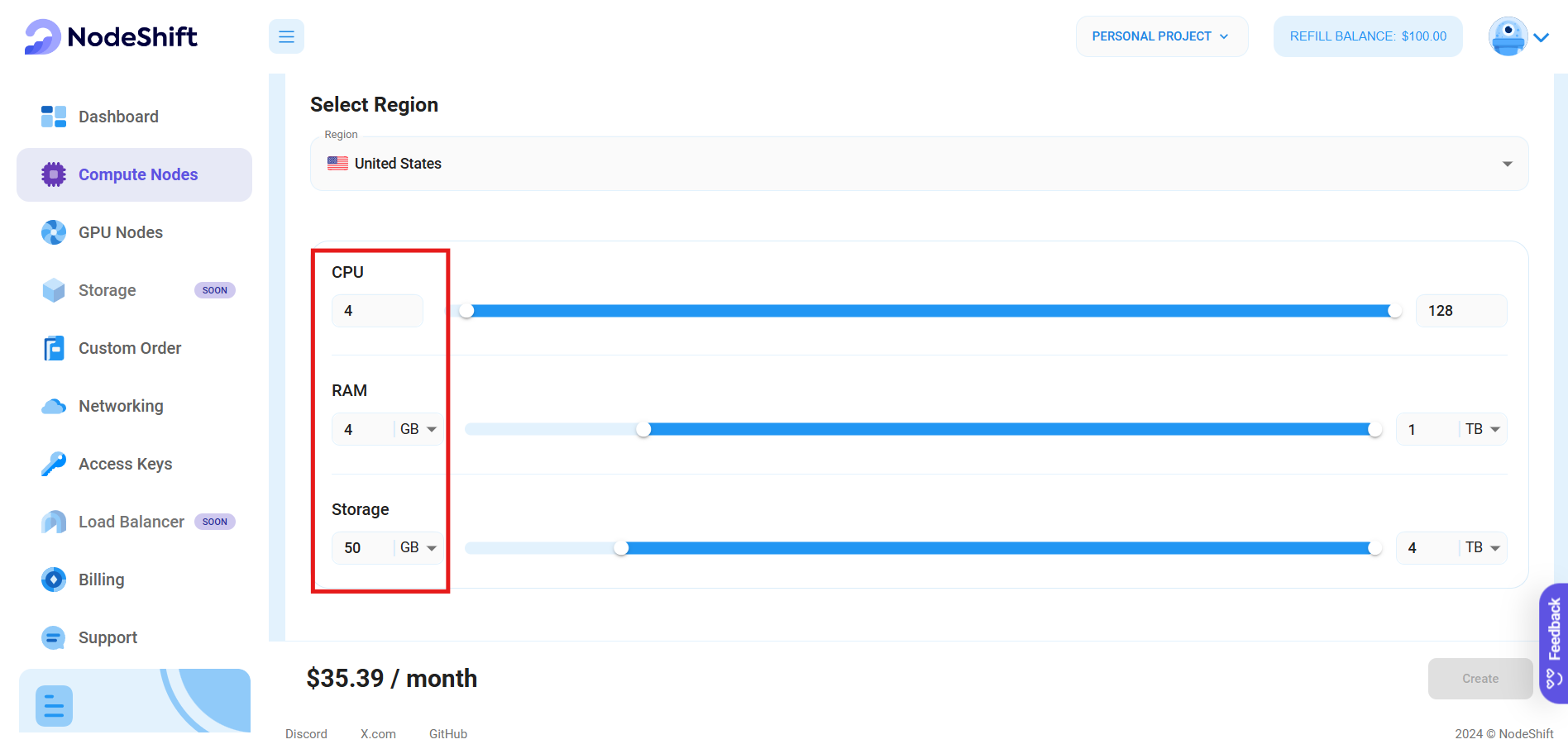
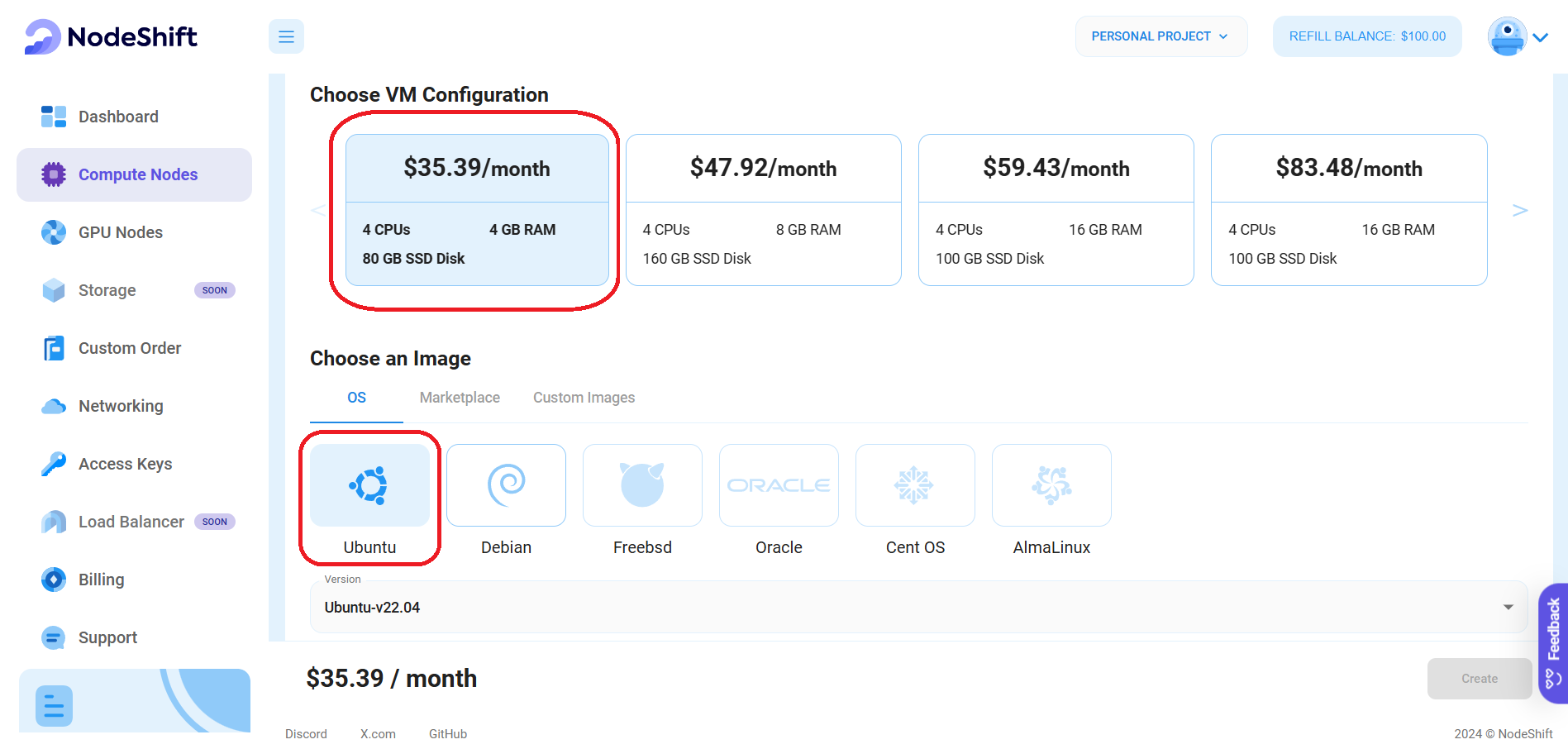
Step 4: Choose VM Configuration and Image
- After you select your required configuration options, you'll see the available VMs in your region and as per (or very close to) your configuration. In our case, we'll choose a '4 vCPUs/4GB/80GB SSD' Compute node as the best possible match.
- Next, you'll need to choose an image for your Virtual Machine. For the scope of this tutorial, we'll select Ubuntu, but you can choose any other option for setting up Grafana.
Step 5: Choose the Billing cycle and Authentication Method
- Two billing cycle options are available: Hourly, ideal for short-term usage, offering pay-as-you-go flexibility and Monthly, best for long-term projects with a consistent usage rate and potentially lower cost.
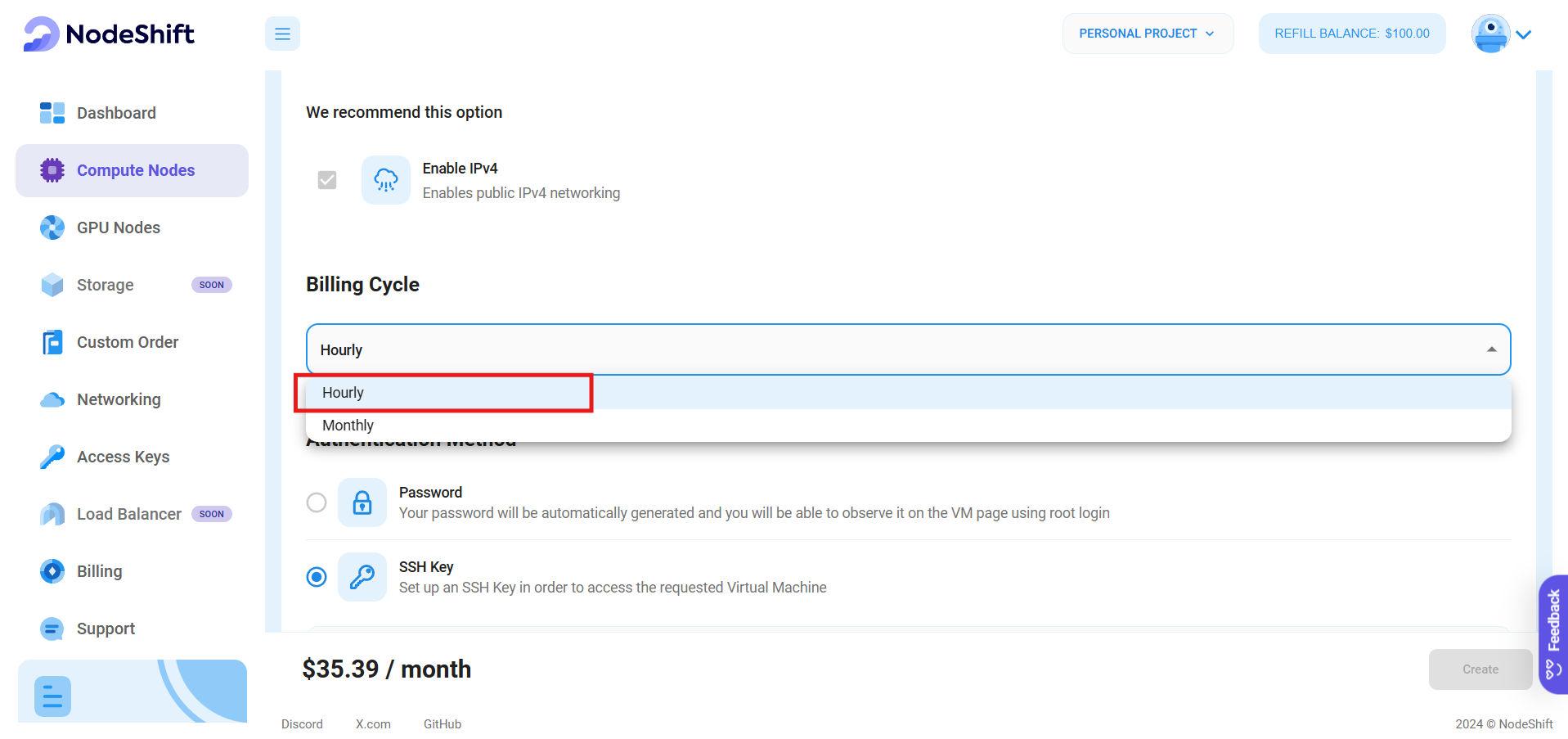
- Next, you'll need to select an authentication method. Two methods are available: Password and SSH Key. We recommend using SSH keys, as they are a more secure option. To create one, you can just head over to our official documentation.

Step 6: Finalize Details and Create Deployment
Finally, you can also add a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), which provides an isolated section for you to launch your cloud resources (Virtual machine, storage, etc.) in a secure, private environment. We're keeping this option as thedefault for now, but feel free to create a VPC according to your needs.
Also, you can deploy multiple nodes at once by clicking + in the Quantity.

That's it! You are now ready to deploy the node. Finalize the configuration summary; if it looks good, click Create to deploy the node.

Step 7: Connect to active Compute Node using SSH
As soon as you create the node, it will take few seconds or a minute to get deployed. Once it is deployed, you will see a status Running in green, meaning that our Compute node is ready to use!
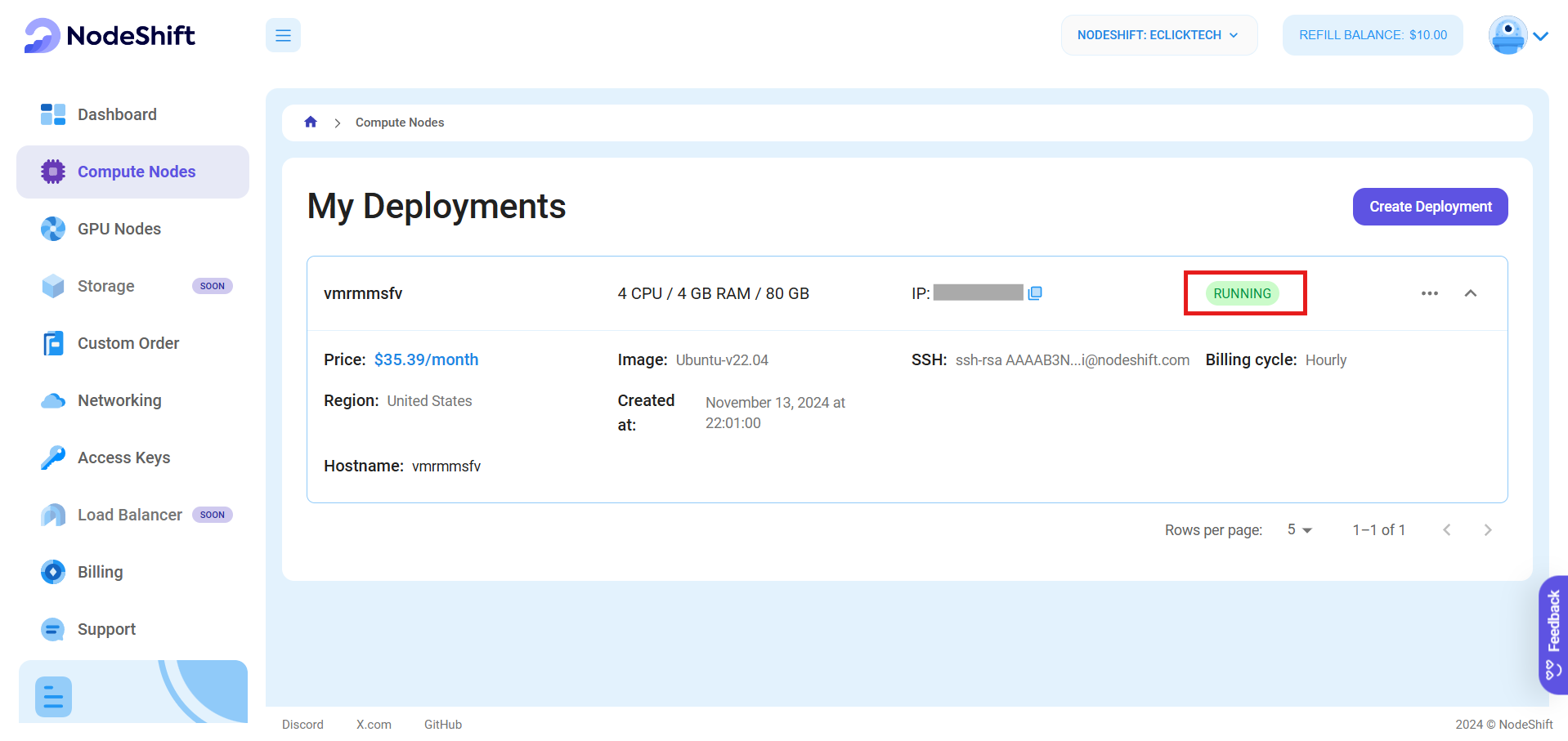
Once your node shows this status, follow the below steps to connect to the running VM via SSH:
- Open your terminal and run the below SSH command:
(replace root with your username and paste IP of your VM in place of ip after copying it from the dashboard)
ssh root@ip
- If SSH keys are set up, the terminal will authenticate automatically.
- In some cases, your terminal may take your consent before connecting, enter 'yes', and you should be connected.
Step 8: Install Dependencies for Grafana
Before we move on to install Grafana, we first need to perform some prerequisites steps to set up dependencies which are required to install Grafana.
- Let's start by updating the Ubuntu package source list for the latest version and security updates
sudo apt updateOutput:
- Install the required packages
sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https software-properties-common wget
Output:
- Add Grafana GPG Key
For secure APT package management, we'll download and store GPG Key using the following commands:
a) Create a directory to store the key
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings/b) Download, convert, and store the key
wget -q -O - https://apt.grafana.com/gpg.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/keyrings/grafana.gpg > /dev/null
- Add Grafana APT repository and update packages again
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/grafana.gpg] https://apt.grafana.com stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list
sudo apt update
Output:
Step 9: Install Grafana
Once you are done with the above steps, you can proceed with the installation of Grafana
sudo apt install grafana
Output:
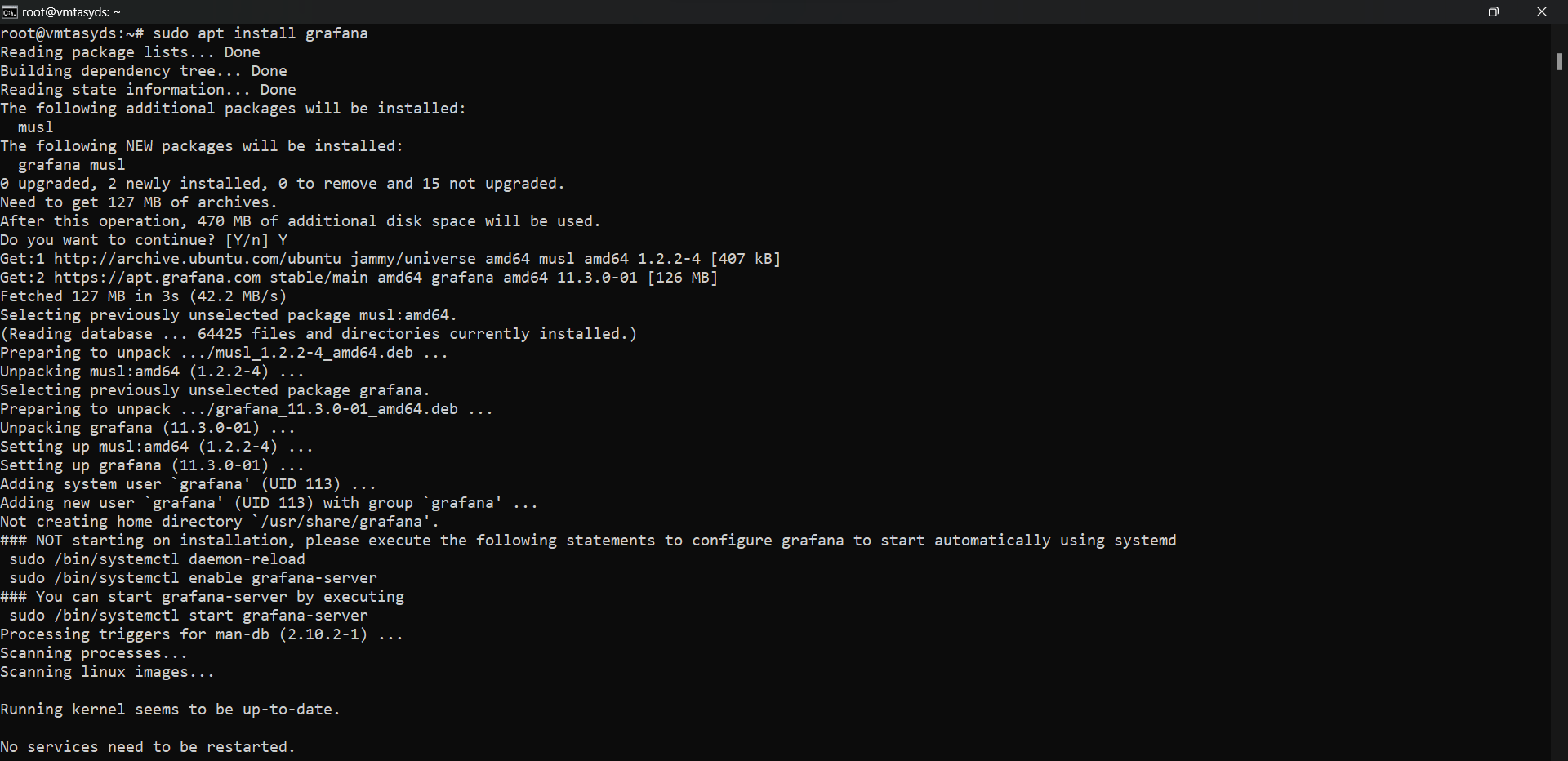
Step 10: Start and Enable Grafana
After the Grafana installation is complete, we will proceed to start and enable Grafana so that we can access its service.
- Let's first verify the installation by logging the version:
sudo grafana-server -v
Output:

- Start Grafana server
sudo systemctl start grafana-server- Enable the server
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server
Output:

- Verify the status
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
Output:
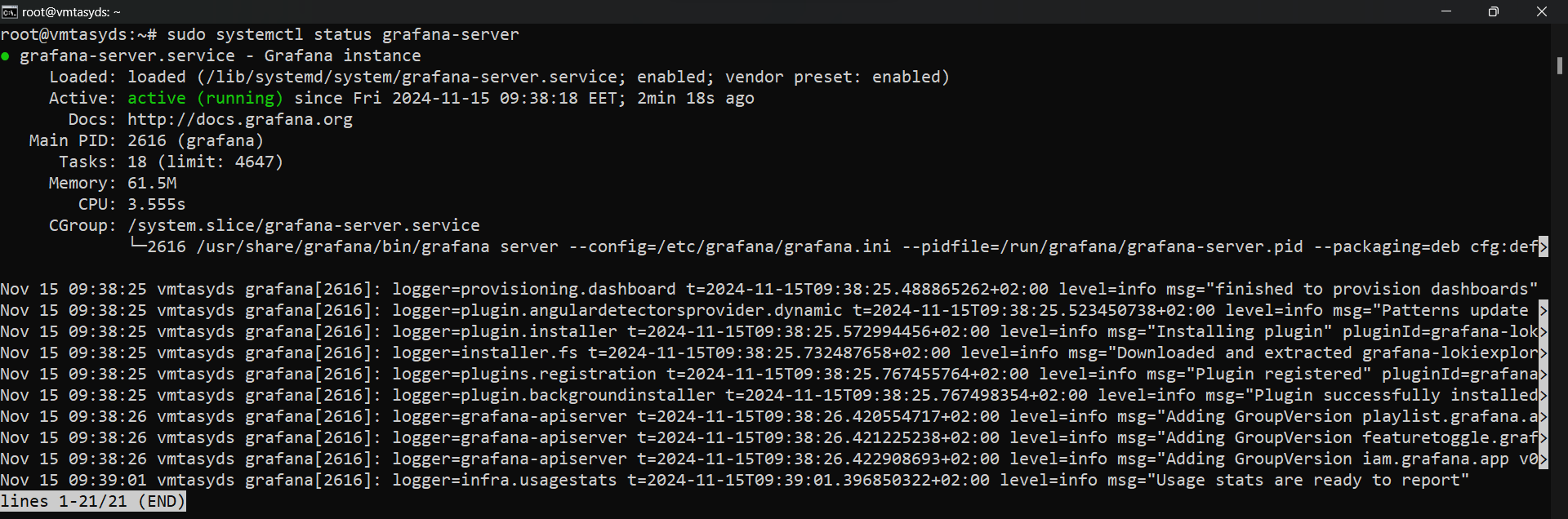
As you can see, our Grafana server is successfully up and running.
Now, let's move on to access the Grafana service and see how the web interface looks like.
Step 11: Access the Grafana Web Interface
Follow the below steps to seamlessly access the Grafana service on your Ubuntu VM and start using it.
- Configure the port on the firewall.
Use the below three commands one by one to enable the firewall and allow access to Grafana
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcpOutput:

- Access the web interface
Open a browser and paste the URL below to access Grafana's web interface
(replace ip with your server's IP address/hostname)
http://ip:3000Once loaded, you should see an interface like this:
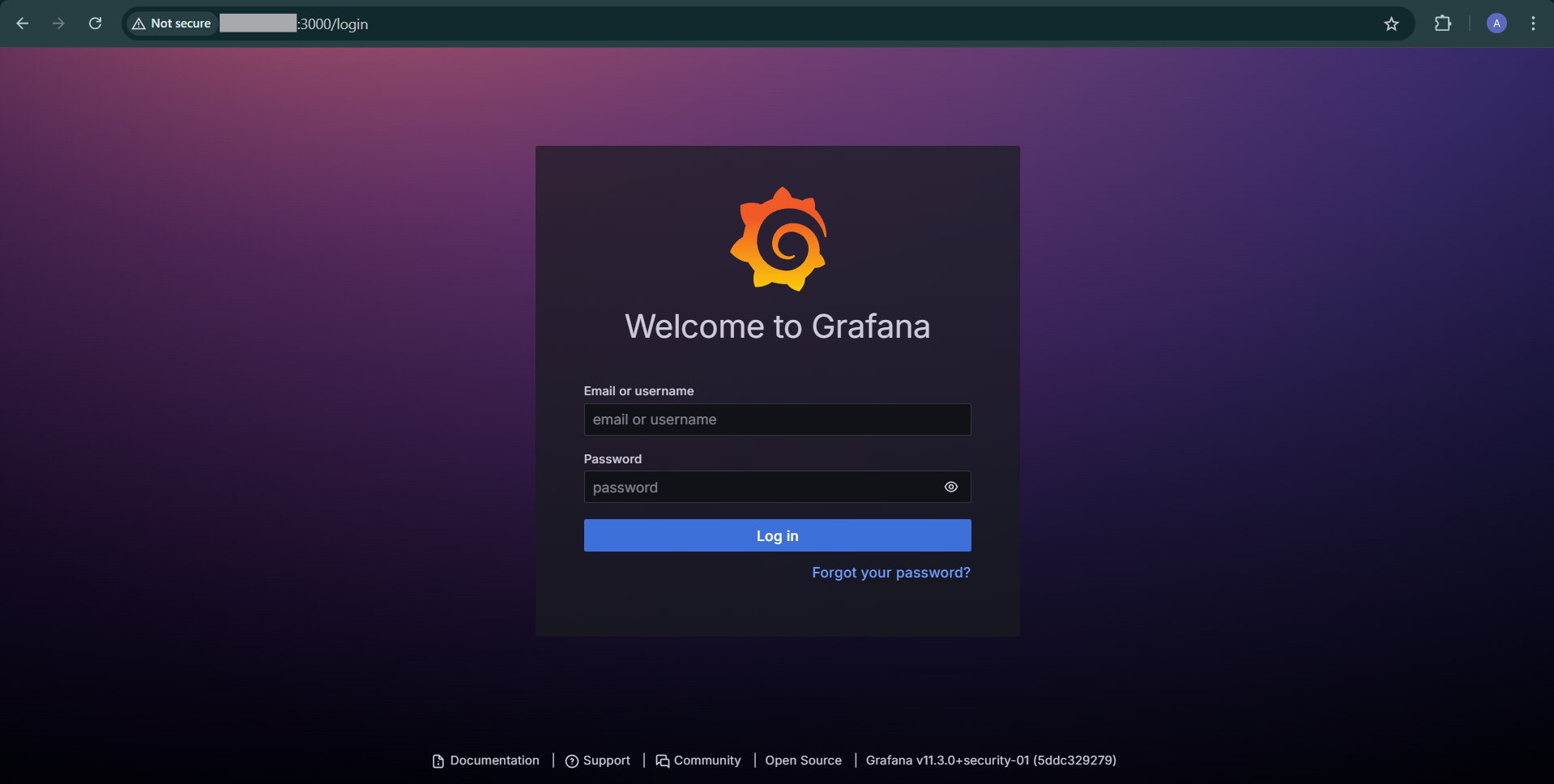
Use the following as your "first-time login" credentials to log in to the dashboard:
- username: admin
- password: admin
After you successfully log in using the above credentials, it will ask you to create your own new password for security concerns.
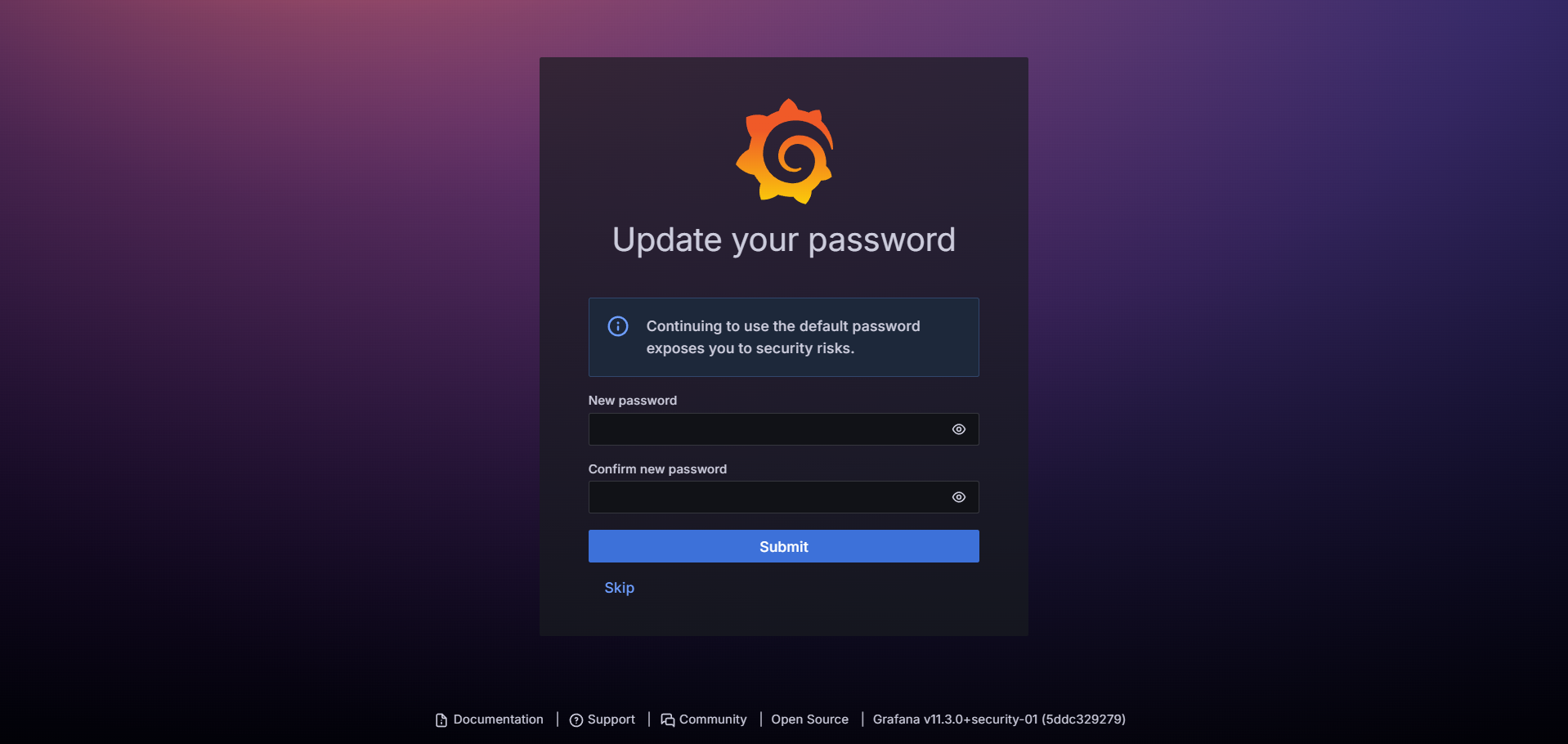
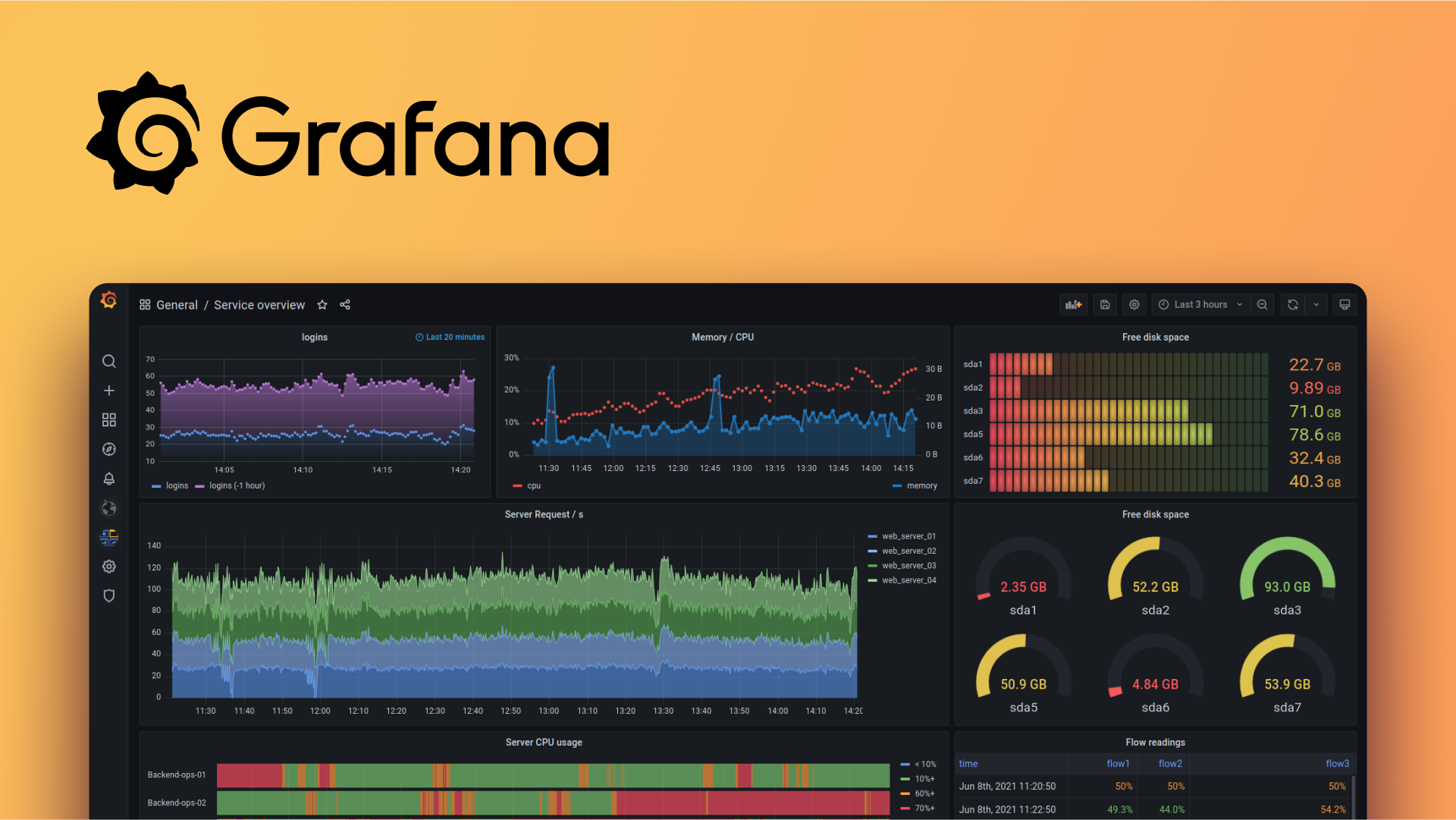
Once you create your new password and submit it, it will take you to Grafana's dashboard, which looks something like this:
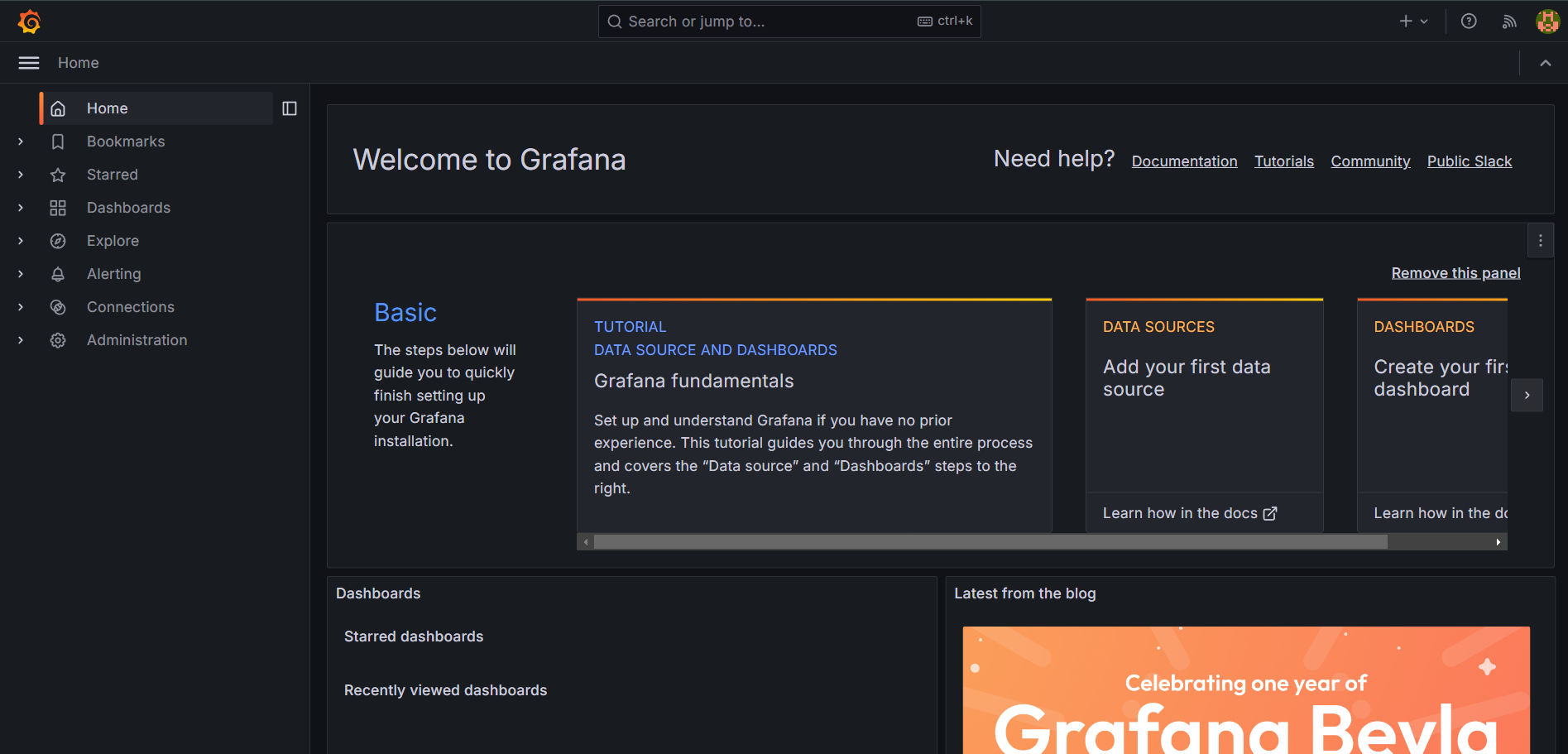
Congratulations, your Grafana web service is successfully set up and ready for you to take your data insights to the next level!
Conclusion
Implementing Data-driven decisions can prove to be very powerful for the growth of a business. A tool like Grafana can double the results when set up and utilized correctly. In this article, we covered an easy and optimized approach to deploying a powerful VM like Ubuntu on NodeShift and setting up a Grafana server on top of it. In addition to saving cost by using an open-source tool like Grafana, this approach enables you to set up a compute-heavy and efficient Ubuntu Virtual Machine on a robust and affordable cloud platform like NodeShift without any up-front costs or technical specialties.
For more information about NodeShift:





